 |
| Step-by-Step: ITI to B.Tech for a Secure Engineering Career |
ITI Fitter vs. Diploma vs. B.Tech: Best Career Path for Mechanical Engineering
This strategy isn’t limited to mechanical engineering. You can apply the same model in other fields too, for example:
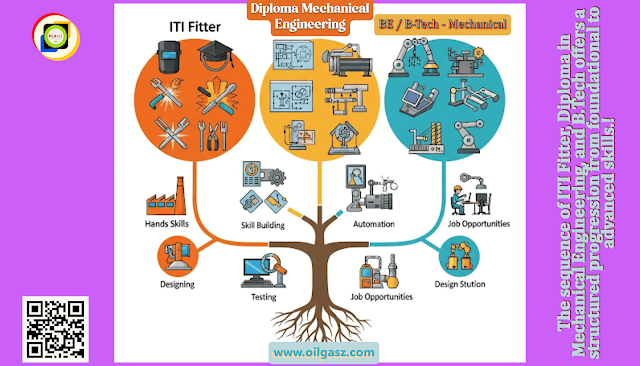
In today's competitive job market, choosing the right educational path is crucial for a successful career in mechanical engineering. The sequence of ITI Fitter, Diploma in Mechanical Engineering, and B.Tech offers a structured progression from foundational to advanced skills.
A Brief Overview of Mechanical Engineering Qualifications in the Government Sector
Career Progression from ITI Fitter to BE/B.Tech Mechanical Engineering
The government sector offers a structured and rewarding career path for mechanical engineering professionals, ranging from an ITI (Industrial Training Institute) Fitter to a BE/B. Tech Mechanical Engineering graduates. This field provides job security, promotions, and long-term growth opportunities, making it an attractive choice for many. Here's why this approach works:
Why Follow the ITI -Diploma-B.Tech Path?
Step-by-Step Skill Building: Start with an ITI Fitter course to gain hands-on technical skills. Follow it with a Diploma in Mechanical Engineering for deeper theoretical knowledge. Finally, pursue a B.Tech for advanced expertise and leadership roles.
Increased Job Opportunities: This path equips you with a wide range of skills, making you eligible for diverse roles in industries like manufacturing, automotive, and more.
Flexibility in Career Levels: Whether you secure an entry-level technician job or a higher-level engineering role, your qualifications ensure better employability.
Backup Plan for Non-B.Tech Aspirants: If you don’t want to pursue a B.Tech., completing an ITI Fitter course and a Diploma still opens doors to stable, skill-based jobs.
1. Entry-Level Positions (ITI Fitter & Diploma Holders)
- PSUs (Public Sector Undertakings)
- Defense (Indian Army, Navy, Air Force as technicians)
- State and Central Government Workshops
- Municipal Corporations
- PWD (Public Works Department)
- BHEL, ONGC, NTPC, and other PSUs
2. Mid-Level Positions (BE/B.Tech Mechanical Engineers)
- Graduate Engineer (BE/B.Tech): Mechanical engineers can apply for higher-level positions such as:
- Assistant Engineer (AE) in PWD, Railways, and PSUs
- Junior Engineer (JE) in some departments (though promotion to AE is faster)
- Technical Officer in DRDO, ISRO, BARC, and other research organizations
- Indian Railways
- CPWD (Central Public Works Department)
- Military Engineering Services (MES)
3. Career Growth & Promotions
- Time-Based Promotions: Government jobs follow a structured hierarchy, ensuring regular promotions based on seniority and performance.
- Departmental Exams: Clearing exams (like LDCE - Limited Departmental Competitive Exams) can fast-track promotions.
- Higher Studies: Pursuing an MTech or MBA can lead to administrative roles like Project Manager or Technical Director.
Key Benefits
Job Security: The combination of practical and theoretical knowledge makes you a strong candidate in the job market.
Career Growth: With qualifications at multiple levels, you can start working early and upskill later for better roles.
Competitive Edge: In a fast-evolving industry, having a mix of certifications increases your chances of landing a job, regardless of market conditions.
While luck may play a role in securing top-tier positions, this educational path ensures you’re well-prepared for a rewarding career in mechanical engineering.
Brief overview of the demand for mechanical engineering qualifications in the government sector.
Highlight the career progression from ITI Fitter to BE/B. Tech Mechanical Engineering.
Purpose of the blog: Guide readers on job opportunities and career paths.
Why Mechanical Engineering Qualifications Are Valued in Government Jobs
Importance of technical skills in government sectors (e.g., railways, PSUs, defense).
Versatility of ITI Fitter, Diploma, and BE/B.Tech qualifications.
The government’s focus is on skilled professionals for infrastructure and industrial projects.
Job Opportunities for ITI Fitter Graduates
Entry-level roles: Technician, Junior Mechanic, Machine Operator.
Key government sectors: Indian Railways, PSUs (e.g., BHEL, SAIL), and Defense (DRDO).
Salary range and benefits (e.g., job security, pensions).
How to apply: SSC, RRB, and PSU recruitment exams.
Career Paths for Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
Mid-level roles: Junior Engineer, Supervisor, Technical Assistant.
Opportunities in government departments: PWD, Irrigation, PSUs.
Exams to target: SSC JE, State JE exams, PSU direct recruitment.
Advantages of diploma holders in technical and supervisory roles.
Opportunities for BE/B.Tech Mechanical Engineers
High-level roles: Assistant Engineer, Executive Engineer, and Management positions.
Key employers: IES (Indian Engineering Services), PSUs (ONGC, IOCL), DRDO.
Career progression to top management roles in government organizations.
Preparation tips: GATE, IES exams, and direct PSU applications.
How to Prepare for Government Jobs
Importance of competitive exams (GATE, SSC JE, IES, RRB).
Recommended study resources and coaching institutes.
Tips for resume building and interview preparation.
Networking and staying updated with government job notifications.
Success Stories
Real-life examples of ITI Fitter, Diploma, and BE Mechanical graduates in government roles.
How their qualifications helped them climb the career ladder.
Inspirational takeaways for aspiring candidates.

